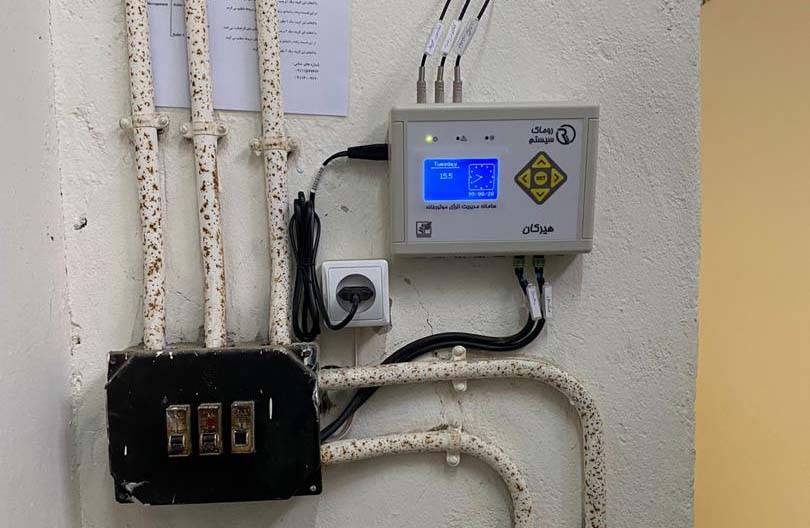

Hirkan smart home engine
by Romak Arian Suspension System Company Spring one thousand four hundred
The Hirkan engine room intelligent control system (a product of Romak, Avijeh Sanat Arian Company) is installed on the engine room without changing the engine room, and it reduces the fuel consumption of the engine room from 25 to 50%. In fact, this system primarily calculates the thermal needs of a building with high accuracy and by adjusting the circulating hot water temperature of the engine room according to the thermal needs, it leads to an increase in efficiency and optimal energy consumption in the engine room. Also, observing the technical considerations and correct management in starting the engine room equipment will lead to an increase in the life of the equipment. This system has outstanding features compared to other similar products and, unlike other products, it can be installed on all types of engine houses.
In the following, the control strategy, the technical specifications of the device and its distinctive features are stated.
Strategy formulated to save and increase productivity
Romak System Avije Sanat Arian Company
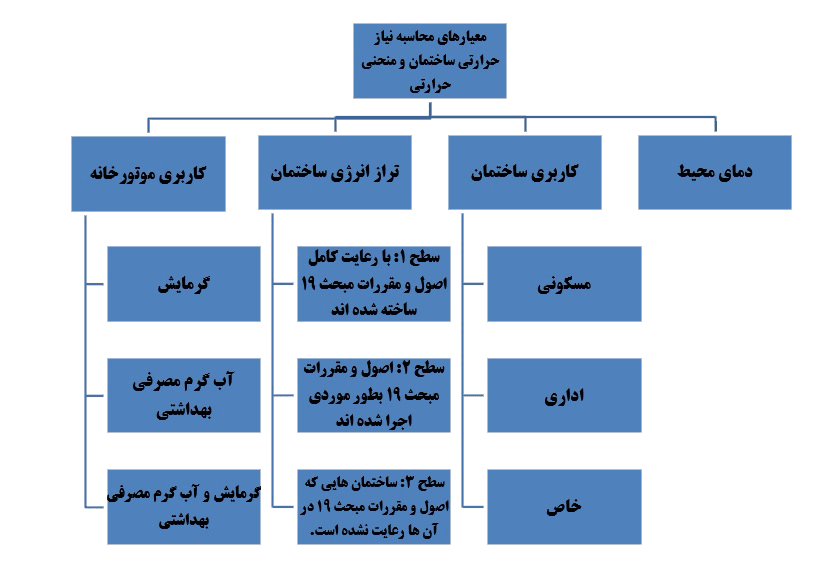
One of the basic problems in engine houses is not adjusting the water temperature of the engine house according to the environmental conditions and the thermal needs of the building. In most cases, the building's heat demand has no proportion to the heat produced by the engine room. Therefore, there are many times when the internal temperature of the building is far from the comfort temperature. In order to adjust the water temperature of the engine room, in the first step, it is necessary to determine how much heat the building needs for heating at any moment of the day. With the research done on the types of engine houses, it was concluded that 4 main parameters play a role more than other parameters in the formula for calculating the thermal requirement of a building.
These 4 indicators are as follows:
- ambient temperature
- Use of engine room Heating supply
- Building energy balance Level 1: Buildings that are built based on the principles and regulations of topic 19 buildings
- building use Residential building
Providing hot water for sanitary consumption
Providing heating and hot water for sanitary consumption
Level 2: Buildings in which the principles and regulations of topic 19 have been implemented in a tasteful manner
Level 3: Buildings in which the principles and regulations of topic 19 are not observed
Office building
Special building
2- Equipment management
The management logic governing this device is Master-Slave type or main and backup type. This means that the engine room capacity is used according to the needs of the building. For example, suppose a motor house has 2 boilers Facing such a system, the device considers one of the boilers as the main boiler and the other as the backup boiler. If the environmental conditions and building conditions are such that one of the boilers has the ability to heat the engine room water to the desired temperature, the second boiler will not enter the circuit, otherwise the device will turn on the second boiler. In the case of engine houses with more than two boilers, it will be controlled and managed with a similar logic but more complicated than the described logic. By using this device in a central engine house that has several boilers, the equipment can be used according to the needs of the building.
3- Schedule
In many government offices, the engine room is kept on during the night to keep the interior of the building warm in the early morning. This issue causes excessive consumption of energy (fuel and electricity) in the engine room. Excessive consumption can be prevented by applying a schedule to turn off and on the engine room.
4- Standby mode
The complete shutdown of the engine room outside of working hours, especially in cold weather, leads to the loss of energy stored in the walls of the building. In such a situation, after turning on the engine room, a lot of energy will be spent to complete the capacitive capacity of the walls of the building. On the other hand, the ambient temperature may be such that the complete shutdown of the engine room is more desirable. The detection of this need is done intelligently in this product, and depending on the diagnosis, the engine room may be on standby or completely shut down during non-working hours.
Hirkan motor home automation
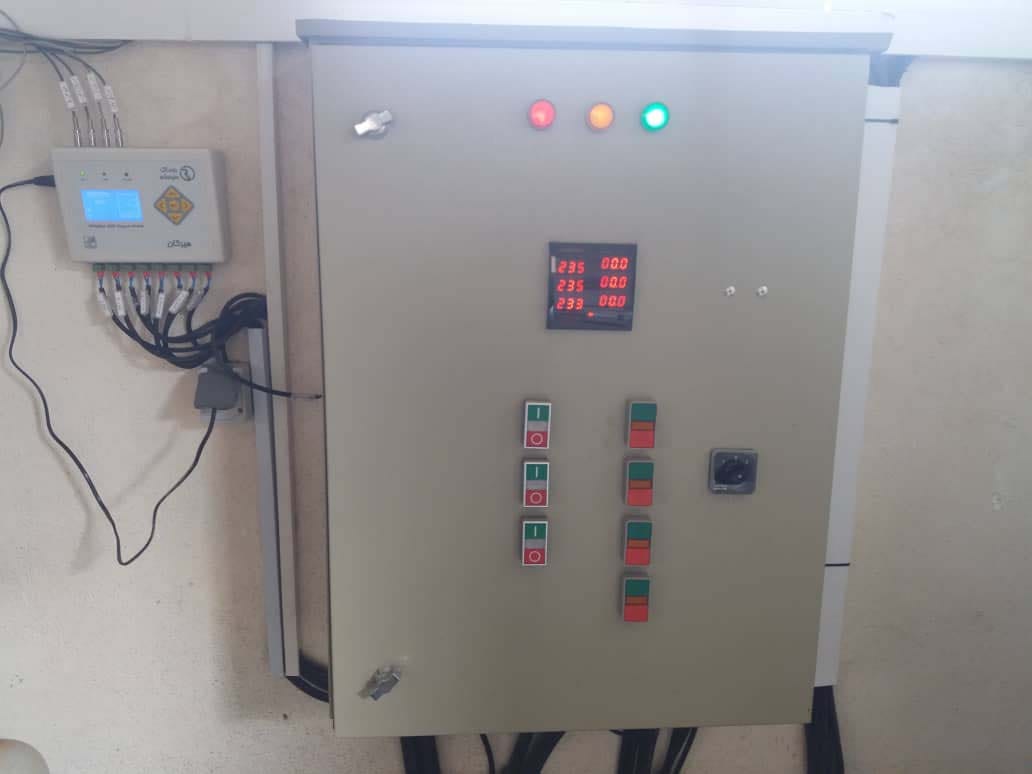

Hirkan model device features and specifications
The features of Romak System's engine room intelligent control device can be expressed in two parts: general features and exclusive features. Generic features include those features that may be found in a similar product, although some features listed in this section are not found in any similar product. The exclusive features of this product include those features that are unique to this device. Many products in the market are out of service after a short period of time due to their defects, and according to studies, the existing products do not fully meet the needs of customers. In fact, the special features of this device have been able to cover these defects well.Functional specifications
- Scheduling program for turning off and turning on the engine room
- Ability to connect to the Internet and apply remote settings
- Ability to transfer data to the central server if necessary
- It has a smart standby program
- Has a control program to turn on pumps and equipment with a time difference
- Ability to automatically troubleshoot equipment and announce it
- Special program for critical conditions in case of disconnection of any of the temperature sensors
Dedicated performance specifications
The ability to introduce the equipment and layout of the engine room to the device through the control panel (if new equipment is added to the engine room, it is possible to control and take possession of it)Support for all types of engine room with different layouts
Separate schedule for each device to turn off and on
Support for boilers with different uses in one engine room and with one device
The management logic governing this device is Master-Slave type or main and backup type. This means that the engine room capacity is used according to the needs of the building
Significant reduction in fuel and electricity consumption due to the special control algorithm
A significant reduction in the amount of greenhouse gases produced
I/O Specifications:
- Working temperature conditions: -20 to +60 degrees Celsius
- Voltage: 100-220V, 0.35A, 50-60Hz
- Audio warning
- Graphic display for monitoring and making settings
- Modbus RTU protocol in RS485 communication platform
- LAN connection for monitoring and applying settings locally
- Digital temperature sensors
- Digital temperature sensors
- 8 output ports and 6 input ports
Protection specifications
7 amp fuse for each outlet to prevent the outlets from drawing too much current and damaging the device's electronic board100 milliampere fuses for each sensor input to prevent damage to other components and disruption of system performance. 2 amp fuse in the 100-240 volt ac input of the device
The internal temperature sensor of the device to measure the temperature inside the device in order to stop the operation and notify the alarm
The series of placing the mechanical thermostat of the boilers in the way of sending the command signal to the burners in order to increase safety
Dimensions
- Length: 200 mm
- Width: 145 mm
- Height: 65 mm
- Weight of the device: 800 grams
Economic and technical achievements of installing the device in the smart engine room

Economic dimension:
- Decreasing gas consumption
- reducing the amount of electricity consumed
- reducing the cost of repairs and maintenance
Technical dimension:
- Increasing the lifespan of equipment (boiler, burner, pump)
- reduction of facility repairs
- Reduction of CO2 greenhouse gas emissions caused by gas fuel
- Keeping the building environment within the comfort temperature range